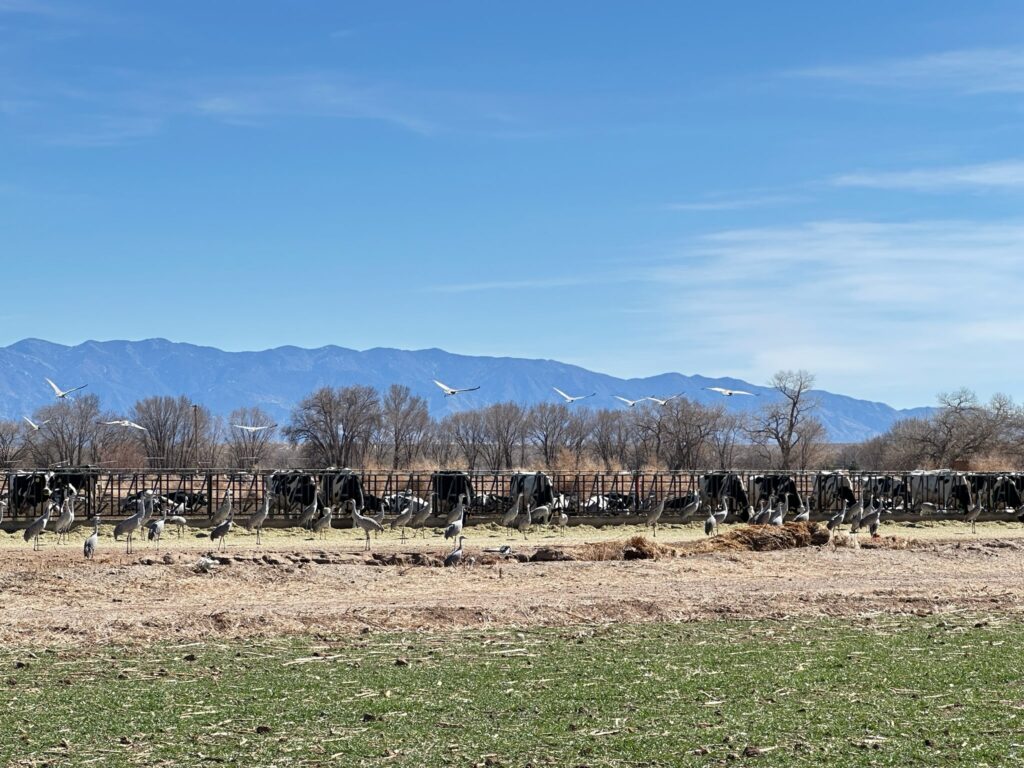
Sandhill cranes like to hang out with the cows sometimes. Photo by L. Heineman.
BERNARDO, NEW MEXICO – The juniper pollen has cranked up early this year, and the irrigators with groundwater pumps (legal or not, it’s hard to know) are firing them up, but the most telling sign of spring was the kettling sandhill cranes this morning.
The term comes from the boiling water in a kettle, as a flock of cranes spirals up in the thermals to conserve energy while they gain altitude for their northward migration. We’d gone down to the state Game and Fish land at Bernardo south of Albuquerque just because, packed lunches and drove down the Rio Grande Valley to look at stuff. We’d seen flocks of snow geese last week when we were driving down to Las Cruces, which triggered a return trip on a lazy family Wednesday.
We saw a few snow goose stragglers at the Bernardo wetland, but their fellows were mostly gone. I worry about stragglers. The cranes, though, were just packing up and heading out, a cacophony as they kettled over the refuge for the trip north.
When we first moved to Albuquerque, in the fall of 1990, we were at a state park along the Rio Grande north of town when we first heard them. I was looking out across the landscape for a turkey farm before I looked up and realized it was these vast flocks, hundreds (thousands?) of huge birds lazing down the flyway to their winter homes.
The cranes are a success story. Near extinction in the 1930s because of human stuff (habitat loss, hunting), the birds are back , hanging out on wildlife refuges, game refuges (they’re popular with hunters) and farms. Check out Lissa’s picture above of the cranes hanging out with the cows at a dairy farm outside Los Lunas. They number now in the tens of thousands now in New Mexico’s Middle Rio Grande Valley each winter.
2025 is gonna be tough on New Mexico’s Rio Grande

Heading to a cooler, wetter place. Photo by L. Heineman
This winter has been dry in the headwaters, and the latest forecast calls for just half of normal flows on the Rio Grande entering New Mexico’s “Middle Valley,” where the cranes and I live. The forecast models, peering out into the middle of March look warm and dry. Beyond that we live in lovestruck hope, but wise planning suggests we should prepare for our hearts to be broken. The cranes are smart enough to head to summer homes in a cooler, wetter place, but we’re stuck here.
It’s too early to do much more than arm-wave about the impact of the low runoff, but this is a blog, so arm-waving is the point. I expect short deliveries to irrigators this year, and I would not be surprised if Albuquerque once again has to switch over to groundwater pumping to keep the taps flowing – my taps – through the heat of summer.
We’ll be fine. We’re used to this. Irrigators will troop down to the irrigation district board meeting the second Monday of each month to complain about not getting water to grow stuff, but there’s a sad resignation to the ritual. We live in a desert. Water is a blessing when it comes, but the reality of desert living requires a stoicism of stubborn acceptance.
The fate of the cranes – from the brink of extinction to the huge kettling flocks we saw this morning at Bernardo – gives me hope, or at least animates my stoic acceptance.
The business model
Inkstain is reader supported. Thanks, y’all.